Surgical Excisions for Benign Lesions
Guardian Dermatology, P.C. | Helena, MT
Mole Excision
(including atypical moles)
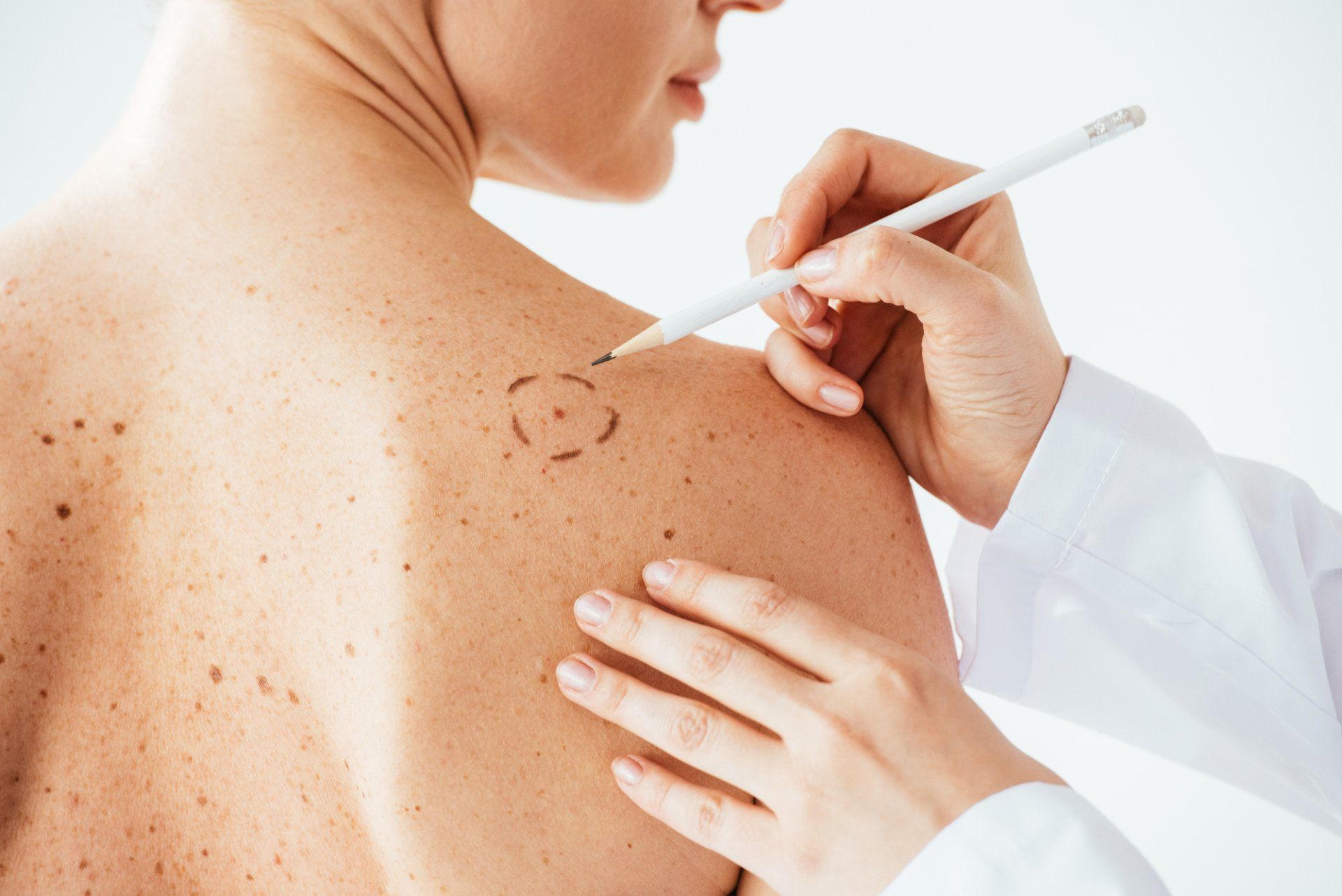
Moles are generally benign growths on the skin that vary in color, from pale pink to dark brown or black. These can appear anywhere on the skin and usually have distinct borders or edges. Sometimes these skin growths become irritated and can be removed to prevent further irritation. Other times, they are removed for cosmetic reasons. While the vast majority of moles are “well-behaved,” there are times we need to removed moles that could be atypical or possibly cancerous in nature (melanoma skin cancer).
Atypical moles are usually larger moles that have unusual features, such as uneven colors and irregularly defined edges. Atypical moles are more of a concern than normal moles because there is a higher risk of melanoma skin cancer developing in patients who have several atypical moles. After a biopsy of an atypical mole, complete removal with excision is sometimes required to ensure that the lesion is entirely gone. However, not all atypical moles need to be removed or re-excised. Should you have an atypical mole biopsied, it is important to have a discussion with your provider regarding the exact nature of your skin lesion and what the current literature supports in terms of best management.
Cyst Excision
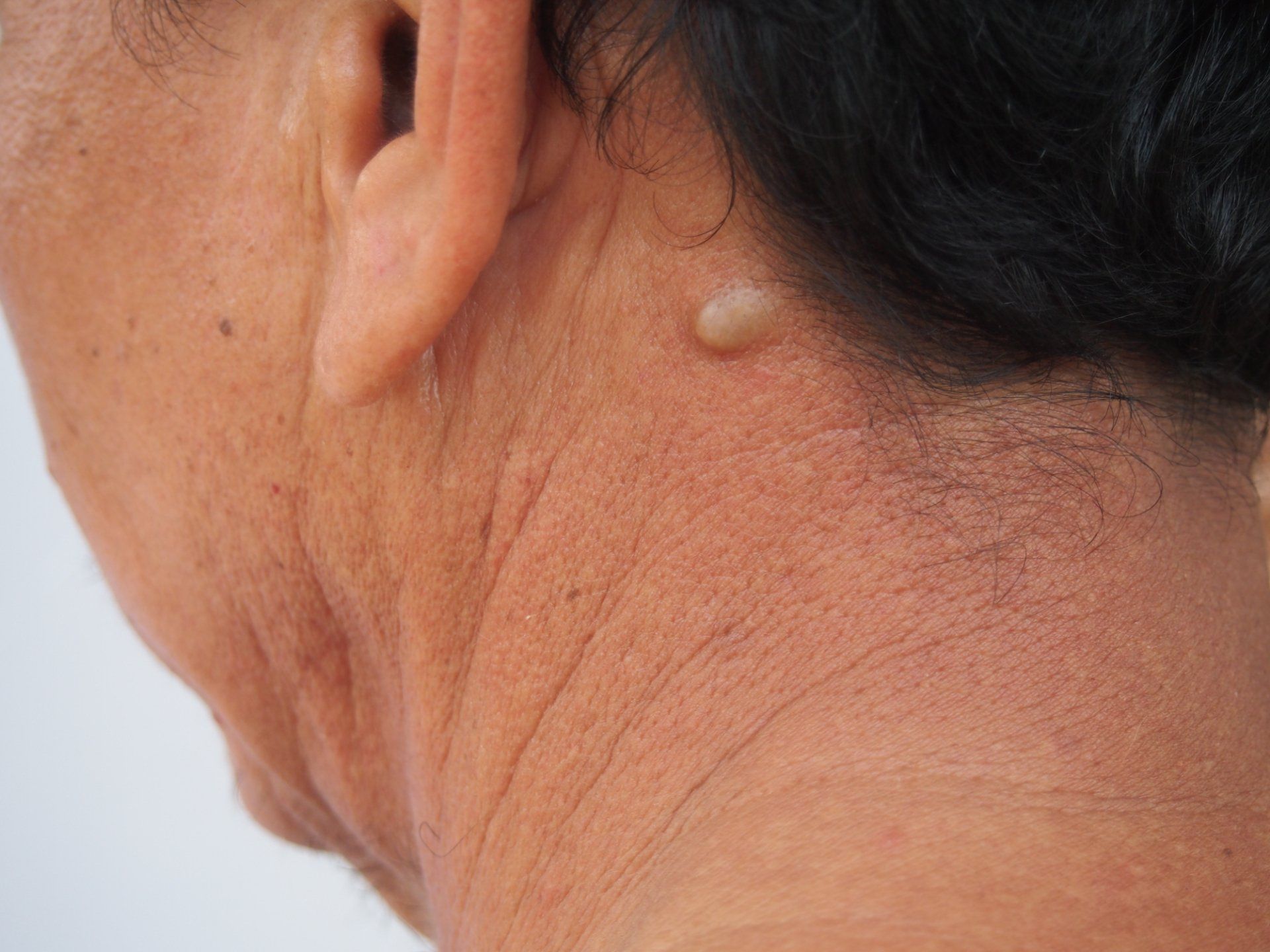
A cyst is growth that forms under the skin, typically consisting of sac-like lining filled with a white, paste-like substance made of dead skin cells and other cell debris. These type of growths can be caused by a variety of factors and can occur anywhere on the body. While cysts are generally benign and are non-cancerous, you may choose to have them removed if they become painful, drain, or frequently become inflamed and/or infected.
Because cysts do not go away on their own, it is best to have them completely removed in one setting if possible. There are several surgical methods used for removing cysts depending on the type of cyst, its size, and its location on the body. After numbing and cleaning the area, the cyst is carefully extracted through the skin. Then, the skin is discreetly sutured with dissolvable or conventional stitches to ensure minimal scarring. It is a short procedure that lasts between 20 to 45 minutes and has a fast recovery time for most patients.
Lipoma Excision
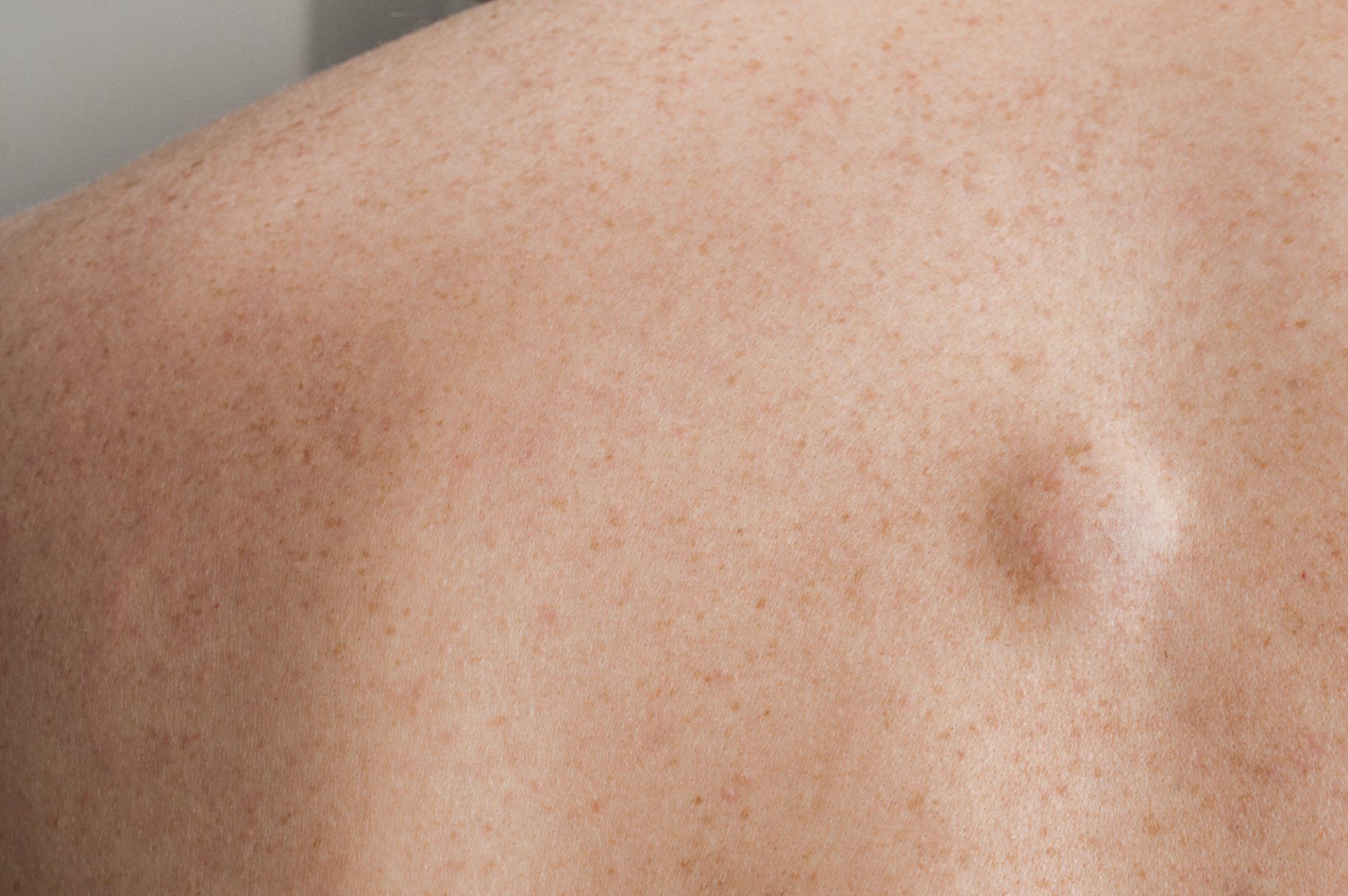
Lipomas are characterized as protruding lumps of fatty tissue that may appear anywhere on the body. These growths are usually soft, benign, and harmless. However, they can occasionally cause an obstruction, feel painful, or have a disfiguring effect if they are located in a highly visible area on the body. Fortunately, you can have your lipomas safely removed if they are bothering you for any reason.
Lipomas are removed via surgical excision. Once the fatty growth is taken out of the body, an empty cavity is left behind. This cavity is immediately sutured and sealed, then the skin above is stitched to completely close the wound. It is a short procedure that lasts between 20 to 45 minutes and has a fast recovery time for most patients.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Excision
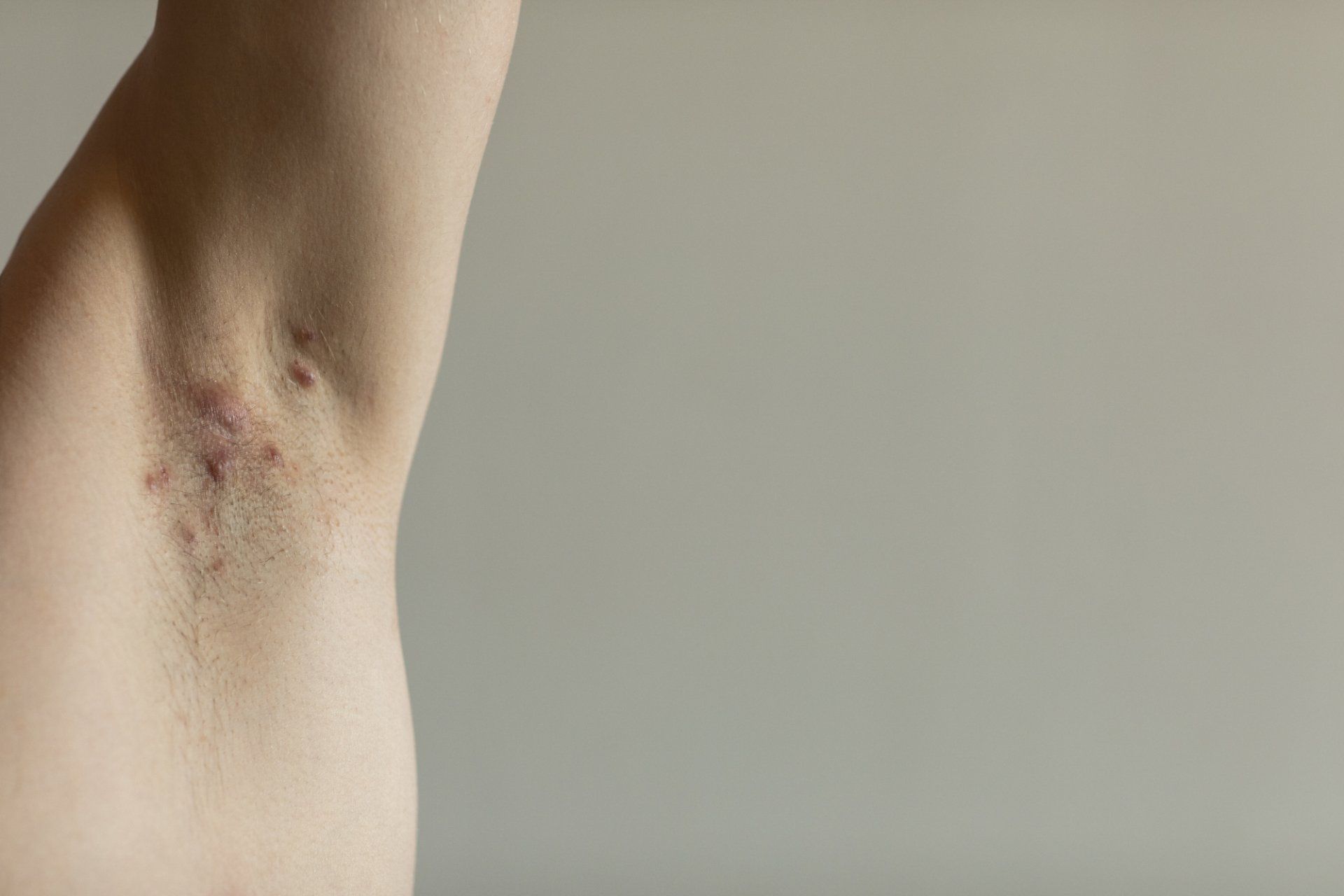
Hidradenitis suppurativa/HS is a chronic abnormal inflammatory skin condition that causes pus-filled wounds to develop under the skin, which later turn into swollen, extremely painful, and sometimes draining areas of skin/scar tissue. The most commonly affected areas on the body include the underarms, under the breasts, buttocks, and the groin. This disorder can be quite difficult to treat and is multifactorial in nature.
The size, number, and severity of your HS lesions will determine the recommended treatment. For larger, chronic areas of disease involvement, or for areas of involvement that have failed other treatments, surgical excision can be a very beneficial option. Wide excision of the involved area is a fairly invasive procedure, but it can be highly effective in treating HS because it completely removes the abnormal involved skin. Once the abnormal skin is removed, it is difficult for the HS to recur in that particular area. Complete removal of HS lesion, when possible, can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life. Other, more minimally invasive surgical options include deroofing (removal of the “roof” or uppermost part of the lesion over the sinus tract/tunnel, then the wound repairs itself with minimal scarring) or injectional therapy.
Schedule an Appointment
Ready to schedule an appointment at Guardian Dermatology? Please call us at 406-272-5941 or click on the button below to get in touch.